Home » Posts tagged 'finance'
Tag Archives: finance
Construction Briefs May 2025
For the 9th consecutive year, I will be speaking at Advancing Preconstruction. I will be opening the program May 22 to the plenary session with a summary of the current and expected economic conditions affecting everyone involved in construction, all geared towards one word, RISK.
Construction Spending Q1’25 vs Q4’24 notable Q/Q increases: Education, Healthcare, Amusement/Recreation and Communication are all up 2% to 3%. Highway is up+4.9%, Data Centers +5.4%, Warehouse +7.5% and Lodging +8.3%.
Construction Spending for March is down 0.5% from Feb, but that’s because Feb was revised UP by 0.5%. Jan also revised up 0.66%. YTD Total vs Jan-Mar 2024 is up 2.8% YTD. Data Centers vs Jan-Mar 2024 is up 40%.
Construction Spending Q1’25 vs Q4’24 is UP in every category except Residential, Commercial/Retail w/o Warehouse and Manufacturing (Mnfg was expected). Residential and Comm/Rtl are down only a slight 0.2% and 0.4%. Manufacturing is down 4.7% Q1vQ4. This is the beginning of the Manufacturing spending taper as early projects come to an end. I described that taper here. The Manufacturing Spending Taper
Not seeing any major indications in spending due to tariffs yet. Still early in the data (thru Mar) for that.
Construction Jobs increased 11,000 in April. However, hours worked dropped by 0.6%. Total workforce hours worked declined by an equivalent of 50,000 jobs. Jobs are now at 8,316,000, an all-time high. Jobs are up 27k year-to-date, the slowest growth for the 1st 4 months since 2012 (excld 2020). Although hours worked fell in April, total workforce hours worked increased 2.1% over same 4mo 2024. Average yr/yr growth for Jan-Apr hours worked is 3.7% for the last 10 yrs (ex 2020).
J P Morgan expects imports from China to fall 75%-80% in the 2nd half of the year. Total all imports from all sources are expected down 20%. Some products are going to become unavailable.
The U.S. imports about 30 million metric tons, about 30% of total steel used, of all types of steel annually. The U.S. imports about 6 million metric tons of steel pipe annually. Approx 2/3rds of steel pipe used annually in the U.S. is imported. If the U.S. loses its imports of steel pipe, we can’t support as many building projects. Pipe here refers to pipe and tube. That includes things like gas and oil pipelines, water pipe, steel conduit and structural square/rectangular tube sections (Trump’s Wall).
What’s frustrating this week is all the latest construction spending and jobs data just came out, and everyone wants to know, What’s the impact on the forecast?, and none of the data reflects tariff impacts or potential slowdowns. Spending is thru Mar31 and jobs are thru Apr12. Some of the inflation data is 1 to 2 quarters behind.
I am expecting, when I prepare the Midyear Forecast, that spending projections will go down, perhaps 1% to 3%, and inflation projections will go up. Currently, I’m carrying inflation between 4%-5%. Owner’s may slow or even cancel capital expenditures and material prices are broadly expected to increase.
When PPI data is released May12, that will be thru April. But remember, PPI data is domestic products only. So any inflation in the PPI data is domestic suppliers adjusting pricing to reflect pricing similar to expected increases to match imports. We might begin to see our first clues of tariff impacts/demand when the next construction starts data gets released around the end of May. How much in previous starts have been canceled/delayed? We already know of some chip plants and data centers canceled/delayed.
Construction – What to Watch: Cost to build going up; Cost to finance is up; Product availability in question; Product delivery schedule delays; Margins pressured; Small/Midsize firms squeezed; Labor let go/disappearing; Projects in planning, delayed; Project ROI not met; Projects planned, canceled.
I recommended (going back 6 yrs ago, but still relevant today) that every construction cost estimator is going to need to identify in every estimate/budget presented to an owner for every upcoming project, all items subject to price revision due to tariff. If you don’t you stand to lose your already meager profits.
I can’t even begin to know what to tell construction cost estimators to carry in budgets for increased cost due to tariffs and supply issues. Best I could suggest at this time is to carry an agreed allowance (IMO, better than contingencies), which can be visited at a later date and adjusted to actual cost. Contingencies are for unknown, unexpected, unidentified issues. Allowances are described in the basis of estimate for identified cost issues, but at unknown cost amounts. All allowances in any estimate/budget should be identified at conception with intent to revisit at later date to adjust to actual cost. (The most common allowance you may be familiar with is a rock allowance). Identify allowances up front and reach agreement on budgeted cost with all parties. This will make your contract administration go a lot smoother than trying to negotiate how much of the contingency you can use for a cost increase that was foreseen. The only unforeseen here is actual cost.
ABI – DMI – CBI Leading Construction Indicators
With exception of residential, which has short durations and for which backlog is always only about 30%-35% of previous yr revenues, for all other work, never (since 2010) was backlog shown to be less than the previous yr spending. https://edzarenski.com/2021/05/01/abi-dmi-cbi-leading-indicators/
Construction Backlog, all work under contract yet to be put-in-place, usually extends out 2 to 3 years. Backlog changes only IF new starts are greater than spending in the month, backlog goes UP. If new starts are less than spending, backlog goes DOWN. Subtract canceled projects from starts causes backlog to go down, but delays are are just moved out in time, so are still in backlog.
PPI INPUTS Q1 vs avg 2024: to Nonres Bldgs +0.9%, to Residential +1.15%, to Highway +1.0%. All these being near 1% for Q1, if growth is constant, would be near 4% for the year. Big IF! Paving mixtures +11% in Q1, Lumber Plywood +4.5%, Fab Str Steel +0.03%, Fab Str Stl Bridges -1.1%, #2 Diesel Fuel -9.6%, Steel Pipe and Tube -3.85%, Nonferrous Wire and Cable +1.8%, Copper and Brass Mill Shapes +4.7%, Aluminum Mill Shapes +7.5%.
PPI Final Demand 1st 3mo vs avg 2024: Avg Nonres Bldgs +1.3%, Educational +1.6%, Healthcare +2.7%, Roofing Contractor + 2.8%, Avg 4 trades +1.7%. Your monthly reminder, although this index is posted monthly, it is corrected quarterly. April data is the correction month for Q1.
New home construction costs have risen about 3% in the last year, from lumber down 4% to concrete up 6%, per JBREC. The US Census Constant Value Rsdn Index is up 3.5% for the 1st 3 months 2025.
The Biden admin supported the construction $200 billion in new manufacturing facilities that began in 2022 and is now tapering down. It will take a lot of jobs to fill those facilities. But will jobs grow in the current economic environment?
Just about anything that can be considered a leading indicator is pointing down. Layoffs, container ship projected offloads are down and falling, China cut shipping to US, supply chains disrupted, immigrant fears affecting labor. Expect costs up, workload down, labor tight.
I’ve been asked, Why don’t you use AI to develop economic analysis? Artificial Intelligence sometimes gets analysis really wrong. There is some percentage (40%?, 60%?) of end results that AI creates that is literally just made up. If you were to use AI to develop forecasts and analysis of construction data, without having a thorough knowledge of the data and an ability to recognize when it’s meaningful, or garbage, then how would you know when AI is right or wrong. Understand your data well enough to know when your analysis makes sense. For my part, I’d rather spend my time understanding the data and the analysis then to spend it verifying if AI is producing realistic and meaningful output.
Summer is just around the corner. The Hummingbirds returned last week.
Construction Briefs – As We Begin 2025
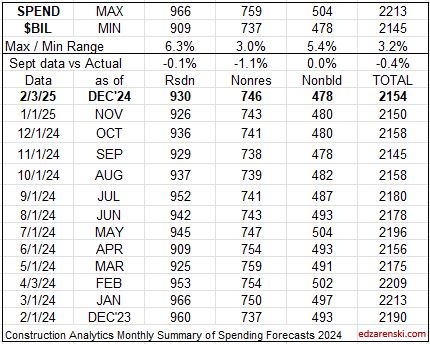
We are close enough, now in mid-January, to see where the numbers will end up for 2024. Construction spending as of Nov is up 6.5% year-to-date vs same 11 months in 2023. We are up 6.0% ytd vs the average of 2023. My forecast predicts we end 2024 up 6.2%, but growth is only 3.4% in 2025.
In February of 2024, with the Dec 2023 data in hand, my forecast for 2024 spending was $2,190 billion, only 1.8% higher than my current (Nov’24 data) forecast of $2,150 billion. Most of that early higher estimate was due to what I carried for my residential forecast, which I have since lowered by 3.6% from the initial forecast at the beginning of 2024. You can see in this monthly summary table that the Nonresidential Bldgs and Non-building forecasts have varied very little and the Total forecast has not varied up or down by more than 0.4% over the last 4 months.
edit 2-3-25 updated table to include Dec data. See the line comparing actual to the SEP data forecast.
Single family construction spending reached a post-2006 high in Q4’21 thru Apr’22 ($480bil). From Apr’22 to the lowpoint in May ’23 ($360bil) spending dropped 25%. By year-end 2023 it had recovered almost 3/4ths of that drop. It fell again in mid-2024 to $410bil, but has since recovered to the year-end’23 level ($450bil). That drop is reflected in the difference between the current forecast and the earlier forecast.
NAHB – Cost of Constructing a Home 2024 excellent summary www.nahb.org/-/media/AB4E…
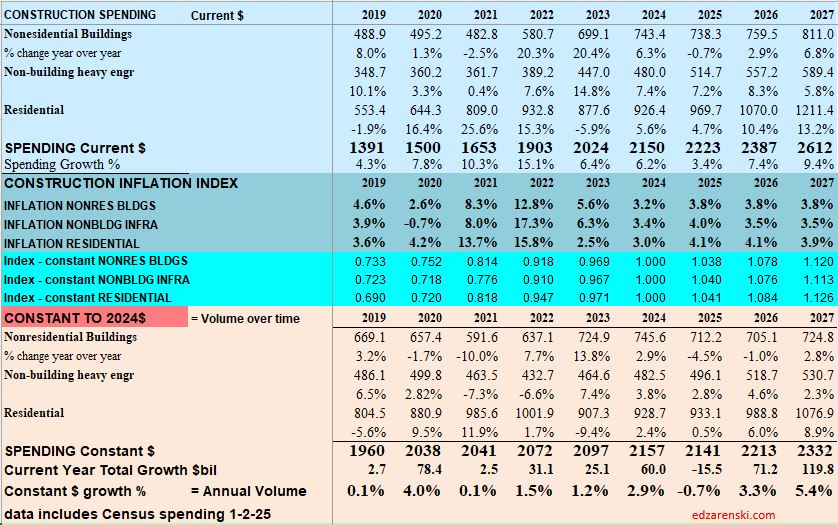
Construction spending in 2024 will hit near $2.15trillion, another new high, up 54% since 2019.
Caution: the following table, showing Constant$ analysis, now shows Constant$ with base year at 2024. Since Q1-2020 I have used the base year at 2019. This update changes the Constant$ amount, but not the Constant$ percent growth. Slight changes in prior years inflation resulted in some minor changes in Constant$ growth.
The last time construction spending declined was 2011. But construction spending includes inflation, which adds nothing to the volume of work put-in-place. Construction volume, (spending minus inflation) will finish the year up only 10% since 2019.
My construction spending forecast for 2025 Nonres Bldgs is down 0.7%. But it’s driven by projects ending in Manufacturing (and Warehouse). In the last 3 yrs, there were $230bil Mnfg starts, most in 2022, $130bil above normal, now some are ending. Without Mnfg, nonres bldgs 2025 spending would be up 4.5%. So while outward appearance may be that nonres spending is declining, in large part it is due to mega spending on Manufacturing buildings (and Warehouse) tapering down upon completion, creating very large annual declines, but normal. See The Manufacturing Spending Taper
Last year at this time, many of the Nonres Bldgs and Non-bldg line items showed Nov-Dec spending was already several points higher than the 2023 average. This was an indication leading into 2024 that those markets were on track to start the year already up. This year,most markets show a decline from the 1st half of the year into the 2nd half. Two notable declines are Warehouse and Office w/o Data Centers. Both start 2025 down 5%+ from the average in 2024.
I didn’t realize how much impact there was with the inclusion of (increasing) Data Centers in the (decreasing) Office construction spending values. I’ve now separated Data Centers from Office and Warehouse from Commercial/Retail. Office spending was pretty strong near it’s highs until 2h’22. Early in ’24 it had fallen to 8%-12% below ’22. Office spending is now 15%-18% below 2022. On the other hand, Data Center spending as of Nov is up 30% from the same months in 2023, and is up more than 60% above the average of 2023 and 120% above 2022. It will continue to increase into 2025.
In 2014-2015, Data Centers was less than 5% of total Office+DC construction spending. Today it is approaching 30%. Next year it will approach 40%. In 2015, Warehouse was 25% of total Commercial spending. By 2022 it had climbed to 54%. In 2025, it will fall back to 45%. Warehouse spending is now decreasing after climbing 100%+ since 2019.
Dodge reports as of Nov construction starts for 2024 up 5% YTD. Residential starts up 7%. Nonresidential Buildings starts up 4%. Non-building starts up 5%.
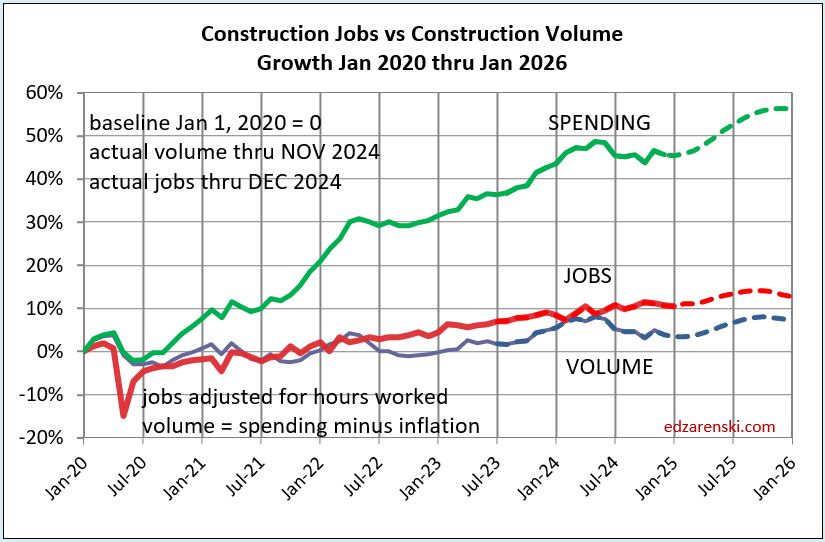
Construction Jobs do not get compared to construction spending. Spending includes inflation, which adds nothing to business volume. Compare jobs growth to Volume growth.
Construction Jobs counts here are the average for the year. That accounts for months during the year, other than Dec/Dec, with higher (or lower) percentage of yr/yr growth. For instance, total jobs Dec24 vs Dec23 increased only by 196k jobs or 2.4%. If you based annual growth on Dec/Dec, it would indicate 2024 increased by 2.4%. However, during the year, jobs growth in Mar-Apr-May were all greater than +3% compared to same month prior year. In fact, every other month during the year had a higher yr/yr growth rate than Dec/Dec. Yearly average of all 12 months shows total jobs annual average up 226K or 2.8%.
Dec/Dec shows a snapshot in time of one month compared to same month last year, without taking into account what might have happened in any of the other 11 months. YR24avg/YR23avg shows the change in the number of jobs over the whole year and accounts for all activity in the year.
Jobs 2024 AVG thru DEC. Rsdn+61k +1.9%. Nonres Bldgs+134k+3.7%. Nonbldg +29k+2.6%
Construction Volume AVG thru NOV Residential +2.9% Nonres Bldgs +3.3% Nonbldg +4.3%.
From 2012-2019, we added a yearly average 245,000 jobs/yr. In 2024 we added 226,000 jobs, but from 2021-2024, we added an average of 247,000 jobs/yr. We add the most jobs in Feb and Mar. We add the least jobs in Apr and Jun. We add more jobs, by far, in the 1st qtr. than any other qtr.
Don’t be surprised if 2025 construction jobs growth slows a bit. Jobs are slightly ahead of volume growth. Since 2019, both Jobs and Volume increased 10%. But that includes 2020, when volume increased 4% but jobs fell by 250k, or 3%. Over the period of 4 years 2021 thru 2024, Jobs increased 13%. Volume of work increased only 6%.
The unemployment rate in construction goes UP in the 1st qtr every year, by 2% to 3% (data since 2011). Now, your 1st thought may be, if unemployment is increasing, that is probably because jobs are falling. Well, construction has ADDED jobs in the 1st qtr. every year since 2011 (excluding 2020), by an avg of nearly 30% of all jobs added annually. More recently, since 2020, we’ve added almost 40% of total annual jobs in Q1. Construction unemployment is not going up in winter months because we lose jobs in winter. So how can the unemployment rate still go up? There’s only one number left in the equation. It goes up because the entire workforce increases by greater than the number of jobs added.
For an example of how this employment timing information can be useful see Employing Correlation – Using construction industry employment data as a proxy for flatbed demand
Harvard Joint Center for Housing Studies posted that In Texas, California, New Jersey, and the District of Columbia, immigrants make up more than half of construction trade workers.
Nov PPI for Construction Mtrls little changed from Oct Inputs YTD to Nonres +0.6%, to Rsdn +1.7%, to Hiway +0.6% Concrete products up 6%, Steel products down 7%-8%, Lumber/Plywood down 2%, Copper up 6%, Diesel down 14%. Final Demand YTD (all in) Nonres Bldgs all up 0.5% or less. Trades up 1%-2%.
We can’t always tell what affect changes in the cost of construction materials will have on the final outcome of annual construction inflation. PPI materials index does not account for productivity or margins and varies on stage of input. A good example of stage of input is PPI for Steel Mill Products. That does not include delivery from mill to fabricator, detailing, fabrication, shop painting, delivery to jobsite, shakeout, lifting, installation and finally overhead and profit, in all about 75% of the cost of structural steel installed.
Construction Analytics Nonres Building Cost Index is a weighted average of eight final cost indices.
NAHB estimates that $184 billion worth of goods were used in the construction of both new multifamily and single-family housing in 2023 and that $13 billon of those goods were imported. eyeonhousing.org/2024/12/impo…
Steel Statistics Cost Increase Effect on Construction? written 2016 US is world’s largest steel importer at 30MMT/yr. 50% from our top suppliers, Canada, Brazil, South Korea and Mexico. China supplies less than 2%. The U.S. annually imports about $2bil from Mexico.
One quarter of all annual Brussel Sprouts consumption occurs around the Christmas holiday.