1-28-20 See the new post Construction Inflation 2020
8-10-19 updated plots and commentary
General construction cost indices and Input price indices that don’t track whole building final cost do not capture the full cost of escalation in construction projects. To properly adjust the cost of construction over time you must use actual final cost or selling price indices.
Click Here for Link to a 20year Table of 25 Indices
Inflation in construction acts differently than consumer inflation. When there is more work available, inflation increases. When work is scarce, inflation declines. A very large part of the inflation is margins, wholesale, retail and contractor. When nonresidential construction was booming from 2004 through 2008, nonresidential final price inflation averaged almost 8%/year. This was at a time when input costs were averaging between 5% and 6%/year. When residential construction boomed from 2003 to 2005, inflation in that sector was 10%/year. But from 2009 through 2012 we experienced deflation, the worst year being 2009. Residential construction experienced a total of 17% deflation from 2007 through 2011. From 2008 to 2010, nonresidential buildings experienced 10% deflation in two years.
The following plots are all the same data. Different time spans are presented for ease of use.


8-10-19 note: this 2005-2020 plot has been revised to include 2018-2020 update.
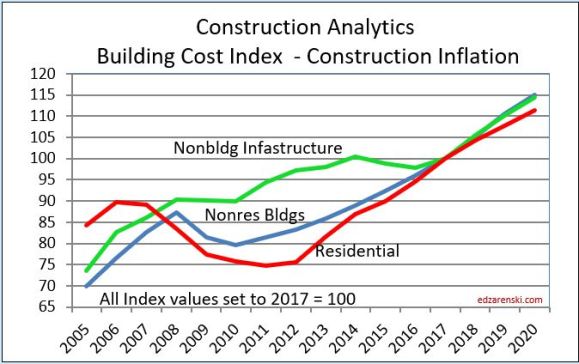
Nonresidential Buildings – Since 1993, the 25-year long-term annual construction inflation has averaged 3.5%, even when including the recessionary period 2007-2011. Long-term average inflation, without recessionary declines, is 4% for 20 non-recessionary years since 1993. During rapid growth period of 5 years from 2004-2008, inflation averaged 8% per year. Since 2011, nonresidential buildings inflation has averaged 3.8%, averaging 4.25%/yr. for the last 4 years with a high of 5.1% in 2018.
Residential, from 2007- 2011 experienced 5 consecutive years of deflation, down 20%. In the 4-year boom just prior to that, 2003-2006, inflation averaged 9% per year. Residential inflation snapped back to 8.0% in 2013. It slowed to 4.4% in 2018 but has averaged over 5% for the last three years.
Construction Spending growth posted two separate 4-year periods of 40%+ growth, up 41% in 2012-2015 and up 40% in 2013-2016, exceeding the growth during the closest similar four-year periods 2003-2006 (+37%) and 1996-1999 (+36%), which were the two fastest growth periods on record with the highest rates of inflation and productivity loss. Growth peaked at +11%/year in 2014 and 2015, exceeded only slightly by 2004-2005.
Spending growth slowed to 7.0% in 2016 and only 4.5% in 2017. In 2018, spending dropped to a gain of only 3.3%. It’s expected, after revisions that 2019 spending will finish at a gain of less than 2%.
Producer Price Index (PPI) Material Inputs (excluding labor) costs to new construction increased +4% in 2018 after a downward trend from +5% in 2011 led to decreased cost of -3% in 2015, the only negative cost for inputs in the past 20 years. Input costs to nonresidential structures in 2017+2018 average +4.2%, the highest in seven years. Infrastructure cost are up near 5% and single-family residential inputs are up 4%. But material inputs accounts for only a portion of the final cost of constructed buildings.
Labor input is currently experiencing cost increases. When there is a shortage of labor, contractors may pay a premium to keep their workers. All of that premium may not be picked up in wage reports. Also, some of the labor inflation is due to lost productivity due to less skilled workforce. Unemployment in construction is the lowest on record. There is some sign of jobs growth slowing down in Q2 and Q3 2019, and potentially getting slower.
Nationally tracked indices for residential, nonresidential buildings and non-building infrastructure vary to a large degree. When the need arises, it becomes necessary that contractors reference appropriate sector indices to adjust for whole building costs.
Click Here for Link to a Table of 25 Index Values
ENRBCI and RSMeans input indices are prefect examples of commonly used indices that DO NOT represent whole building costs, yet are widely used to adjust project costs. An estimator can get into trouble adjusting project costs if not using appropriate indices. The two input indices for nonresidential buildings did not decline during the 2008-2010 recession. All other final cost indices dropped 6% to 10%.
From 2010 to 2019, total final price inflation is 110/80 = 1.38 = +38%. Input cost indices total only 106/85 = 1.25 = +25%, missing a big portion of the cost growth over time.

CPI, the Consumer Price Index, tracks changes in the prices paid by urban consumers for a representative basket of goods and services, including food, transportation, medical care, apparel, recreation, housing. This index in not related at all to construction and should never be used to adjust construction pricing. Historically, Construction Inflation is about double the CPI. However for the last 5 years it averages 3x the CPI.
Taking into account the current (Jan 2018 12 mo) CPI of 2% and the most recent 5 years ratio, along with accelerated cost increases in labor and material inputs and the high level of activity in markets, I would consider the following forecasts for 2018 inflation as minimums with potential to see higher rates than forecast.
Residential construction, from 2007- 2011, experienced five consecutive years of deflation, down 20%. In the 4-year boom just prior to that, 2003-2006, inflation averaged +9% per year. Residential construction inflation saw a slowdown to only +3.5% in 2015. However, the average inflation for five years from 2013 to 2017 is 6%. It peaked at 8% in 2013. It climbed back over 5% for 2016 and reached 5.8% in 2017. For 2018, residential final cost inflation indexes are up only 4.5%. Residential construction inflation for 2019 is now about 4% to 4.5%.
A word about Hi-Rise Residential. About 95% of the cost of a hi-rise residential building would remain the same whether the building was for residential or nonresidential use. This type of construction is totally dis-similar to low-rise residential, which in large part is stick-built single family homes. Therefore, a more appropriate index to use for hi-rise residential construction is the nonresidential buildings cost index.
Nonresidential Buildings inflation, during the rapid growth period of five years from 2004-2008, averaged 8% per year. Inflation averaged near 4% per year for the 4 years 2014-2017.
Several Nonresidential Buildings Final Cost Indices averaged over 5% per year for the last 2 years and over 4% per year for the last 5 years. Nonresidential buildings inflation totaled 22% in the last five years. Input indices that do not track whole building cost would indicate inflation for those four years at only 12%, much less than real final cost growth. For a $100 million project escalated over those four years, that’s a difference of $8 million, potentially underestimating cost.
Nonresidential buildings spending slowed from 2017 to 2019 but is now entering a phase in which it may reach the fastest rate of growth in three years, which historically leads to accelerated inflation. Construction inflation for nonresidential buildings for 2018 and 2019 was 5%/yr. For 2020 expect 4.25%, rather than the long term average of 3.5% to 4.0%.
Non-building infrastructure indices are so unique to the type of work that individual specific infrastructure indices must be used to adjust cost of work. The FHWA highway index increased 17% from 2010 to 2014, stayed flat from 2015-2017, then increased 6%+ in 2018. The Highway index for 2019 is up about 6%. The IHS Pipeline and LNG indices increased in 2018 but are still down 20% since 2014. Coal, gas, and wind power generation indices have gone up only 6% in seven years. Refineries and petrochemical facilities have dropped 5% in 4 years but 2018 regained the level of 2013. Input costs to infrastructure are down slightly from the post recession highs, but most have increased in the last year. Input cost to Highways are up 5.0% and to the Power sector are up 3.6% in 2018. Work in Transportation and Pipeline projects has increased dramatically in 2017 and 2018.
Infrastructure power indices registered 2.5% to 3.5% gains in 2017 and again in 2018. Highway indices increased 6.6% in 2018. Anticipate 4% inflation for Power sector and at least 5%-6% inflation for Highway in 2019 with the potential to go higher in rapidly expanding markets, such as pipeline or highway.
This plot for nonresidential buildings only shows bars representing the predicted range of inflation from various sources with the line showing the composite final cost inflation. Note that although 2015 and 2016 have a low end of predicted inflation of less than 1%, the actual inflation is following a pattern of growth above 4%. The low end of the predicted range is almost always established by input costs, while the upper end of the range and the actual cost are established by selling price indices.
8-10-19 note: this 2005-2020 plot has been revised to include 2018-2020 update.

A word about terminology: Inflation vs Escalation. These two words, Inflation and Escalation, both refer to the change in cost over time. However escalation is the term most often used in a construction cost estimate to represent anticipated future change, while more often the record of past cost changes is referred to as inflation. Keep it simple in discussions. No need to argue over the terminology, although this graphic might represent how most owners and estimators reference these two terms.

In every estimate it is always important to carry the proper value for cost inflation. Whether adjusting the cost of a recently built project to predict what it might cost to build a similar project in the near future or adding an escalation factor to the summary of an estimate for a project with a midpoint 2 years out, or answering a client question, “What will it cost if I delay my project start by one year?”, whether you carry the proper value for escalation can make or break your estimate.
- Long term construction cost inflation is normally about double consumer price inflation (CPI).
- Since 1993 but taking out 2 worst years of recession (-8% to -10% total for 2009-2010), the 20-year average inflation is 4.2%.
- Average long term (30 years) construction cost inflation is 3.5% even with any/all recession years included.
- In times of rapid construction spending growth, construction inflation averages about 8%.
- Nonresidential buildings inflation has average 3.7% since the recession bottom in 2011. It averaged 4.6% for the 4 years 2016-2019.
- Residential buildings inflation reached a post recession high of 8.0% in 2013 but dropped to 3.5% in 2015. It averaged 4.6% for the 4 years 2016-2019, but is at the low point of 3.3% in 2019.
- Although inflation is affected by labor and material costs, a large part of the change in inflation is due to change in contractors/suppliers margins.
- When construction volume increases rapidly, margins increase rapidly.
- Construction inflation can be very different from one major sector to the other and can vary from one market to another. It can even vary considerably from one material to another.
Construction cost estimation must be performed individually for each project. This approach is very different from assembly line manufacturing.
LikeLike
I think this is an informative post and it is very useful.
LikeLike
Very helpful. I am wondering how would you adjust forecasted construction costs that are in current (forecasted) year dollars to dollars expressed in a particular base year (e.g., adjust 2025 cost figures in to 2018 dollars)? Thank you.
LikeLike
Example: What is cost in mid 2019 for a nonresidential building whose midpoint of construction was 2013? Divide Index for 2019 by index for 2013 = 109.6/86.0 = 1.27. Cost of building in 2013 times 1.27 = cost of same building in 2019.
For future work, I would use the long term average idex for the type of work.
See the very end of the post “Construction Inflation Index Tables” for the complete explanation of “How to use an index.”
LikeLike
Thanks so much! I will take a look at that post well.
LikeLike
Excellent information. Would you be able to comment on the inflation rates specifically in N. CA over the past 5 years? It seems it’s been much higher than 4-5% just due to the amount of activity. Thanks.
LikeLike
Kelly, I wouldn’t doubt inflation has been greater on No. Cal. Inflation rates specific to metropolitan areas is a consulting service as considerable research is involved. edz
LikeLike
The rate is a bit better in Europe. It’s somewhere around 3% in most European countries.
LikeLike